Understanding Fabric Coating Types: Wax Coated vs PU Coated vs PVC Coated
Choosing the Right Fabric Coating for Industrial Use
When sourcing technical textiles for demanding environments, the type of coating applied to a fabric can directly impact its durability, performance, and suitability.
Whether you’re designing industrial curtains, heavy-duty tarpaulins, or eco-conscious bags, understanding the differences between fabric coating types, wax, PU, and PVC is essential to making an informed decision.
In this guide, we’ll decode the three most commonly used coatings in the technical textile industry: Wax Coated Fabric, PU Coated Fabric, and PVC Coated Fabric.
We’ll break down their performance, sustainability, ideal use cases, and help you determine which one is best for your application.
What is Fabric Coating?
Fabric coating is a process where a protective layer is applied to textiles to enhance specific properties like water resistance, UV protection, chemical resistance, and durability.
This layer can be applied via techniques such as lamination, spraying, or dipping.
Coated fabrics are essential in sectors such as:
- Industrial safety and PPE
- Outdoor furniture and covers
- Logistics and transport (tarps, truck curtains)
- Environmental containment (oil booms, spill barriers)
Let’s take a closer look at each coating type.
Wax Coated Fabric
Wax Coated Fabric typically uses paraffin or beeswax applied to cotton or canvas, resulting in a breathable, rugged material.
Pros:
- Naturally water-repellent (but not fully waterproof)
- Breathable and flexible
- Biodegradable and environmentally friendly
- Ages well with a vintage patina
Cons:
- Needs re-waxing periodically
- Can melt or transfer wax at high heat
- Limited resistance to chemicals and abrasion
Best For:
- Canvas bags
- Outdoor workwear
- Heritage military/hunting gear
- Eco-conscious brands
PU Coated Fabric
PU (Polyurethane) Coated Fabric involves applying a flexible, rubber-like polymer layer over base fabrics such as nylon or polyester.
Pros:
- Lightweight and flexible
- Moderate waterproofing and breathability
- Softer feel than PVC
- Can be made with water-based PU for eco-friendliness
Cons:
- Less resistant to abrasion and harsh chemicals
- UV degradation over time
- Mid-range durability
Best For:
- Backpacks
- Medical textiles and light industrial covers
- Rainwear and windbreakers
- Tents and awnings
PVC Coated Fabric
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) coating is a thick plastic-based layer applied for heavy-duty protection.
Pros:
- Completely waterproof and weather-resistant
- High resistance to abrasion and chemicals
- Fire-retardant options available
- Long-lasting even in harsh environments
Cons:
- Heavier and stiffer
- Poor breathability
- Not biodegradable; less eco-friendly
Best For:
- Truck tarpaulins and conveyor belt covers
- Industrial curtains and dividers
Spill containment equipment
Fabric Coating Comparison: Wax vs PU vs PVC
Feature | Wax Coated Fabric | PU Coated Fabric | PVC Coated Fabric |
Water Resistance | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
Breathability | High | Medium | Low |
Flexibility | High | High | Medium |
Durability | Moderate | Good | Excellent |
Eco-Friendliness | High | Medium | Low |
UV Resistance | Low | Medium | High |
Maintenance | Needs Re-waxing | Low Maintenance | Easy to Clean |
Use Case Examples | Bags, Jackets | Backpacks, Rainwear, Tents | Tarps, Curtains |
Wax vs PU: Which Should You Choose?
- Choose Wax Coated Fabric if you’re creating lifestyle or reusable items where aesthetics, breathability, and sustainability matter.
- Choose PU Coated Fabric when you need a lightweight, moderately waterproof material for wearable or portable uses.
How to Choose the Right Coated Fabric
Selecting the right coated fabric goes beyond comparing technical specs; it requires a clear understanding of your specific application environment, performance expectations, regulatory standards, and cost constraints.
Key Considerations for Selection:
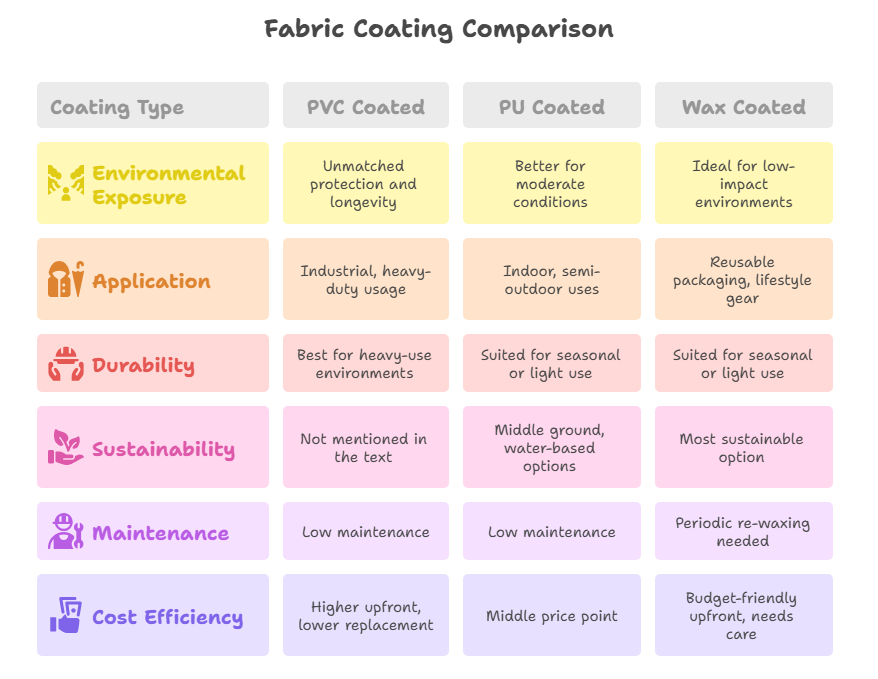
- Environmental Exposure:
- For continuous outdoor exposure, including rain, sun, and chemicals, PVC Coated Fabric offers unmatched protection and longevity.
- For moderate conditions with some need for flexibility and lightweight construction, PU Coated Fabric is a better fit.
- In low-impact environments where natural aesthetics and breathability are valued, Wax Coated Fabric is ideal.
- Application Type:
- Wax Coating suits applications like bags, reusable packaging, lifestyle gear, and eco-friendly branding.
- PU Coating is suitable for indoor or semi-outdoor uses such as backpacks, tent linings, medical mattress covers, or light-duty covers.
- PVC Coating is your go-to for industrial curtains, truck tarps, oil containment systems, and heavy-duty usage.
- Durability Needs:
- Evaluate the frequency of use and expected lifecycle. For heavy-use environments, PVC wins. For seasonal or light use, PU or Wax might suffice.
- Sustainability Goals:
- If environmental impact is a major concern, Wax Coated Fabric is the most sustainable option.
- PU Coatings, especially those made with water-based formulations, offer a middle ground.
- Maintenance Expectations:
- Some buyers prefer materials that require little upkeep. PVC and PU-coated fabrics are low-maintenance. Wax Coated Fabrics, while charming, demand periodic re-waxing.
- Cost Efficiency:
- PVC may involve higher upfront costs but lower long-term replacement frequency.
- PU sits at a middle price point with good balance.
- Wax Coated may be budget-friendly upfront, but it needs long-term care.
Helpful Questions to Ask Before Finalizing Your Choice:
- Will the fabric need to maintain performance across multiple weather cycles?
- Are aesthetics or branding a major concern?
- Does the end-use require frequent washing, cleaning, or sanitation?
- What is the average wear-and-tear expected from this application?
By evaluating these parameters, procurement managers and product designers can select a coating that aligns with both operational and environmental priorities.
Below is the table that you can refer to while selecting the right fabric as per your use case.
Requirement | Recommended Coating |
Rugged aesthetics | Wax Coating |
Lightweight flexibility | PU Coating |
Harsh environments | PVC Coating |
Eco-friendliness | Wax Coating |
Medical or hygiene use | PU Coating |
Long-term outdoor use | PVC Coating |
Still unsure? Ask yourself:
- Will the fabric be exposed to UV or chemicals?
- Is weight a concern?
- Is environmental impact a priority?
Conclusion
Each fabric coating type offers distinct advantages. Wax is sustainable and breathable, PU balances comfort and performance, and PVC stands out in extreme conditions.
Still unsure about your choice? Check out our complete fabric coating comparison or speak to our technical experts for help with your selection.
FAQs
1. Which fabric coating is most waterproof?
PVC Coated Fabric offers the highest waterproofing due to its thick, plastic-based barrier.
2. Is wax-coated fabric durable for daily use?
Yes, but it requires re-waxing every 6-12 months, depending on exposure and use.
3. Are PU coatings environmentally safe?
Some PU coatings use water-based solvents, making them more eco-friendly than PVC, but not as biodegradable as wax.
4. Can I use PVC Coated Fabric outdoors?
Absolutely. It performs well in UV, rain, and harsh chemical environments.
5. Which coating is best for reusable packaging?
Wax Coated Fabric is breathable, natural, and sustainable; ideal for reusable bags and eco-conscious packaging.
6. What’s best for industrial warehouse dividers?
PVC Coated Fabric; thanks to its abrasion resistance, waterproofing, and ease of cleaning.
Contact Information
- Mon - Sat: 10:00am-7:00pm
- 4/32-33 Triveni Nagar , Meerpur Cantt , Kanpur-208004
- +91 9839708040 | +91 9936159591
- gncfabrics@gmail.com
Quick Links
- About Us
- Products
- Blog
- Contact Us
© 2024 GNC EXPORTS, All rights reserved. Developed by DIGI PEXEL
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Cookies Policy
